Organizational Cynicism and Turnover Intention in Hotel Industry at Delhi
Abstract
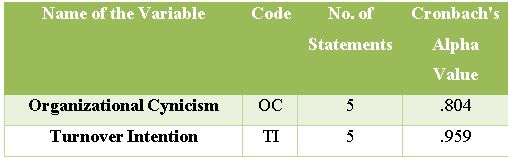
The current study focuses on the hotel industry in Delhi, to gauge the association between organizational cynicism and turnover intention and to check statistically whether the association is significant or not. The adapted questionnaire was the medium to capture the information related to the study and respondents were employees working in the hotel industry in Delhi. 249 samples from the population were analysed with the help of SPSS (version 20). Reliability and factor analysis was found suitable in preliminary analysis. Thereafter, Simple Linear Regression analysis was applied to report the association between the variables of the current study. Researchers have reported a poor and positive association, which was statistically insignificant. It was the inference that organizational cynicism behaviour has no effect on turnover intention in the hotel industry at Delhi, although such feelings are prevailing among the employees. The findings of the study will make aware to the owners of business firm to minimize such attitude which detriments the performance of employees and organization, whiles shortcomings will provide the direction to identify the gap for further research.
Downloads
References
Abraham, R. (2000). Organizational cynicism: Bases and consequences. Genetic, Social and General Psychology Monographs. 126(3), 269-292. PMID: 10950198. [Article]
Adams, J. S. (1965). Inequity in social exchange. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, New York: Academic Press.
Ay, F. A. & Unal, O. (2016). The relationships between psychological contract, organizational cynicism and turnover intention. Journal of International Health Sciences and Management, 2(1), 102-112. [Article]
Bateman, T. S., Sakano, T. & Fujita, M. (1992). Roger, me, and my attitude: Film propaganda and cynicism toward corporate leadership. Journal of Applied Psychology, 77, 786-771.Doi:10.1037/0021-9010.77.5.768[Crossref]
Beheiri, L. A., Ahmed, E. S., & Aboul-Ela, G. M. B. E., (2018). Analyzing the effect of organization cynicism on intention to leave: A case study on Nola Cupcakes. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 20(6), 20-26. DOI: 10.9790/487X-2006052026[Crossref] [Article]
Dean, J., Brandes, P., & Dharwadkar, R. (1998). Organizational cynicism. The Academy of Management Review, 23(2), 341-352. Doi:10.2307/259378 [Crossref]
Dreher, G. F. (1982). The role of performance in the turnover process. Academy of Management Journal, 25(1), 137-147. [Article]
Eaton, J. A. (2000). A social motivation approach to organizational cynicism. York University Toronto, Ontario.
George, D., & Mallery, P. (2003). SPSS for windows step by step: A simple guide and reference. 11.0 update (4th ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Goldner, F. H., Ritti, R. & Ference, T. (1977). The production of cynical knowledge in organizations. American Sociological Review. 42(4), 539-551. Doi: 10.2307/2094553 [Crossref]
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., Anderson, R. E., & Tatham, R. L. (2006). Multivariate data analysis (6th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Qualification Inc.
Hutcheson, G., & Sofroniou, N. (1999). The multivariate social scientist. London: Sage.
Iqbal, A. (2013). Impact of job autonomy and supervisor’s and co-workers’ support on job burnout and satisfaction: The mediating role of emotional labor. The International Journal of Economics and Management Sciences, 2(6), 67-73. [Article]
Kaiser, H. F. (1974). An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika, 39, 31-36. Doi:10.1007/BF02291575 [Crossref]
Karatepe, O., Yavas, U., & Babakus, E. (2007). The effects of customer orientation and job resources on frontline employees' job outcomes. Services Marketing Quarterly, 29(1), 61-79. Doi:10.1300/J396v29n01_04 [Crossref]
Khan, M. A. (2014). Organizational cynicism and employee turnover intention: Evidence from banking sector in Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Commerce and Social Sciences, 8(1), 30-41. [Article]
Mobley, W. H., Horner, S. O., & Hollings Worth, A. T. (1978). An evaluation of precursors of hospital employee turnover. Journal of Applied Psychology, 63 (4), 408-414. Doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.63.4.408 [Crossref]
Mohamad, A. H., & Aizzat, M. N. (2006). Predicting turnover intention of hotel employees: The influence of employee development human resource management practices and trust in the organization. Gadjah Mada International Journal of Business, 8(1), 21- 42. Doi:10.22146/gamaijb.5625 [Crossref]
Nair, P., & Kamalanabhan, T. J. (2010). The Impact of cynicism on ethical intentions of Indian managers: The moderatıng role of seniority. Journal of International Business Ethics, 3(1), 14-29. [Article]
Nunnaly, J. (1978). Psychometric theory. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Ozler, D. E., & Atalay, C. G. (2011). A research to determine the relationship between organizational cynicism and burnout levels of employees in health sector. Business and Management Review, 1(4), 26-38. [Article]
Rehman, O., Karim, F., Rafiq, M., & Mansoor, A. (2012). The mediating role of organizational commitment between emotional exhaustion and turnover intention among customer service representatives in Pakistan. African Journal of Business Management, 6(34), 9607-9616. DOI: 10.5897/AJBM11.2411 [Crossref] [Article]
Shahzad, A., & Mahmood, Z. (2012). The mediating-moderating model of organizational cynicism and workplace deviant behavior: Evidence from banking sector in Pakistan). Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 12(5), 580-588. DOI: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2012.12.5.1612 [Crossref], [Article]
Shore, L. M., Tetrick, L. E., Lynch, P., & Barksdale, K. (2006). Social and economic exchange: Construct development and validation. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 36(4), 837-867. Doi:10.1111/j.0021-9029.2006.00046.x[Crossref]
Srivastava, A., & Adams, J. W. (2011). Relationship between cynicism and job satisfaction: Exploration of mechanisms. Psychological Reports, 108(1), 27-42. Doi:10.2466%2F02.07.09.14.PR0.108.1.27-42 [Crossref]
Tavakol, M., & Dennick, R. (2011). Making sense of Cronbach’s alpha. International Journal of Medical Education, 2, 53-55. DOI: 10.5116/ijme.4dfb.8dfd [Crossref]
Tükeltürk, S. A., Perçin, N. S., & Güzel, B. (2012). Psychological contract breaches and organizational cynicism at hotels. The Young Economists Journal, 9(19), 194-213. [Article]
Volpe, R. L., Mohammed, S., Hopkins, M., Shapiro, D., & Dellasega, C. (2014). The negative impact of organizational cynicism on physicians and nurses. The Health Care Manager, 33(4), 276-288. DOI: 10.1097/HCM.0000000000000026 [Crossref]
Wanous, J. P., Reichers, A. E., & Austin, J. T. (2000). Cynicism about organizational change: Measurement, antecedents and correlates. Group and Organization Management, 25(2), 132-153. Doi:10.1177%2F1059601100252003 [Crossref]
Zimmerman, R. D., & Darnold, T. C. (2009). The impact of job performance on employee turnover intentions and the voluntary turnover process: A meta‐analysis and path model. Personnel Review, 38 (2), 142-158. Doi:10.1108/00483480910931316 [Crossref]
Copyright (c) 2021 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS, BUSINESS AND HUMAN BEHAVIOUR

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.











